Dr Susan Brown
Department: Comparative Biomedical Sciences
Campus: Camden
Research Groups: Musculoskeletal Biology
Sue joined the RVC in January 2010 as Reader in Translational Medicine. The focus of Sue's work is to understand the muscle, eye and brain phenotype of a group of muscular dystrophies known as the 'secondary dystroglycanopathies'; which are forms of neuromuscular disease characterised by the altered glycosylation of alpha dystroglycan.
Sue studied Zoology with Botany at the University of Reading followed by a PhD in Muscle Development at The Royal Veterinary College. Since this time Sue has held appointments at the Royal Free Hospital, Guys’ Hospital Medical School, Royal Holloway College and Imperial College, London.
A MRC Career Development Grant whilst at Imperial enabled Sue to develop models for forms of muscular dystrophy linked to the altered glycosylation pattern of alpha dystroglycan (the dystroglycanopathies); work which she now continues at The Royal Veterinary College. Defects in the basement membranes of the eye, brain and muscle characterise the severe end of the clinical spectrum which is unusually wide in this group of disorders. Sue's main focus is in understanding how alterations in basement membrane formation lead to eye, brain and muscle involvement of some patients but not others who present solely with a muscular dystrophy. The ultimate goal of this work is to devise ways of intervening in the disease process.
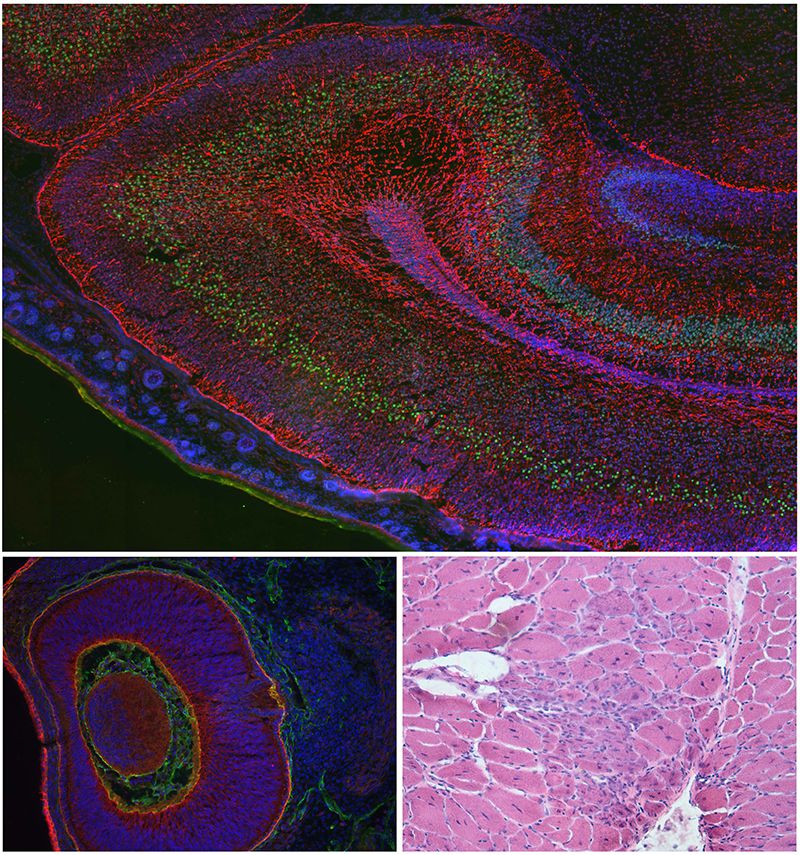
The Brown laboratory focuses on the pathogenesis of brain, eye and muscle defects in the dystroglycanopathies
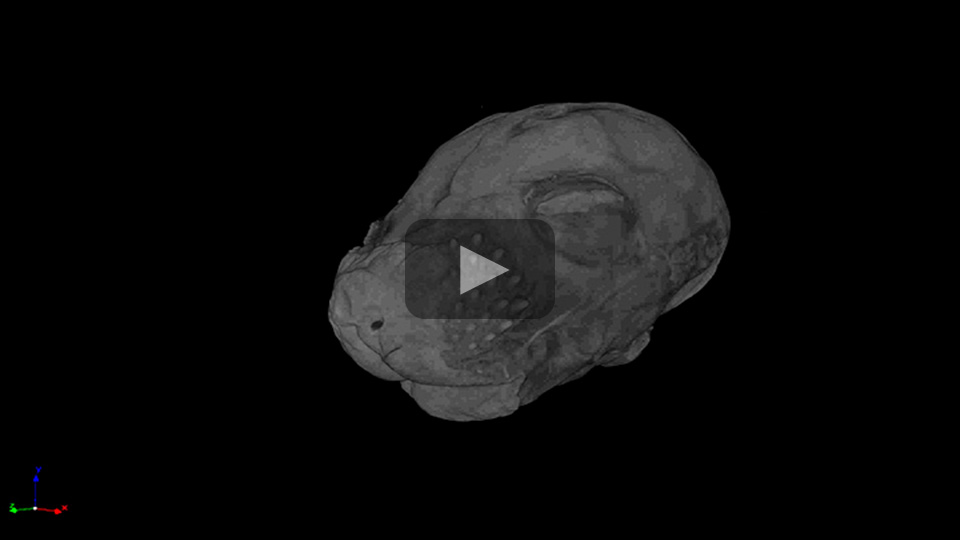
The video below shows how microCT can be used to evaluate the brain and eyes of dystroglycanopathy mouse models.
Booler HS, Pagalday-Vergara V, Williams JL, Hopkinson M, Brown SC. Evidence of early defects in Cajal Retzius cell localisation during brain development in a mouse model of dystroglycanopathy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2016 Dec 31. doi: 10.1111/nan.12376. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 28039900
Hildyard JC, Lacey E, Booler H, Hopkinson M, Wells DJ, Brown SC. (2016) Transgenic Rescue of the LARGEmyd Mouse: A LARGE Therapeutic Window? PLoS One. 2016 Jul 28;11(7):e0159853. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159853. eCollection 2016. PMID: 27467128
Kim J, Hopkinson M, Kavishwar M, Fernandez-Fuente M, Brown SC. (2016) Prenatal muscle development in a mouse model for the secondary dystroglycanopathies. Skelet Muscle. Feb 19;6:3. doi: 10.1186/s13395-016-0073-y. eCollection 2015.
H.S. Booler, J.L. Williams, M. Hopkinson, S.C. Brown (2015) .Degree of Cajal-Retzius cell mislocalisation correlates with the severity of structural brain defects in mouse models of dystroglycanopathy. Brain Pathology, 2015 Aug 26. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12306. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 26306834
Humphrey EL, Lacey E, Le LT, Feng L, Sciandra F, Morris CR, Hewitt JE, Holt I, Brancaccio A, Barresi R, Sewry CA, Brown SC, Morris GE.(2015). A new monoclonal antibody DAG-6F4 against human alpha-dystroglycan reveals reduced core protein in some, but not all, dystroglycanopathy patients. Neuromuscul Disord. 2015 Jan;25(1):32-42. Epub 2014 Sep 16.
Whitmore, C., Fernandez-Fuente, M., Booler, H., Parr, C., Kavishwar, M., Ashraf, A., Lacey, E., Kim, J., Terry, R., Ackroyd, M. R. Wells KE, Muntoni F, Wells DJ, Brown SC (2014). The transgenic expression of LARGE exacerbates the muscle phenotype of dystroglycanopathy mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. Apr 1;23(7):1842-55.
Fernandez-Fuente, M., Martin-Duque, P., Vassaux, G., Brown, S. C., Muntoni, F., Terracciano, C. M. and Piercy, R. J. (2013). Adenovirus-mediated expression of myogenic differentiation factor 1 (MyoD) in equine and human dermal fibroblasts enables their conversion to caffeine-sensitive myotubes. Neuromuscul. Disord. Mar;24(3):250-8
Waite, A., Brown, S. C. and Blake, D. J. (2012). The dystrophin-glycoprotein complex in brain development and disease. Trends Neurosci. 35, 487-496.
Ross, J., Benn, A., Jonuschies, J., Boldrin, L., Muntoni, F., Hewitt, J. E., Brown, S. C. and Morgan, J. E. (2012). Defects in glycosylation impair satellite stem cell function and niche composition in the muscles of the dystrophic Large(myd) mouse. Stem Cells 30, 2330-2341.
Ackroyd, M. R., Whitmore, C., Prior, S., Kaluarachchi, M., Nikolic, M., Mayer, U., Muntoni, F. and Brown, S. C. (2011). Fukutin-related protein alters the deposition of laminin in the eye and brain. J. Neurosci. 31, 12927-12935.
Muntoni, F., Torelli, S., Wells, D. J. and Brown, S. C. (2011). Muscular dystrophies due to glycosylation defects: diagnosis and therapeutic strategies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 24, 437-442.
Ackroyd, M. R., Skordis, L., Kaluarachchi, M., Godwin, J., Prior, S., Fidanboylu, M., Piercy, R. J., Muntoni, F. and Brown, S. C. (2009). Reduced expression of fukutin related protein in mice results in a model for fukutin related protein associated muscular dystrophies. Brain 132, 439-451.
Sue contributes to the BSc Biological/Bioveterinary Sciences and BVetMed Courses. She is module leader for the Imaging of Disease.